Insulinoma
Forest Washington, MD
The Operative Review of Surgery. 2023; 1:155-161.
Table of Contents
Pathophysiology
Also Known as “Beta Cell Neoplasm”, “Beta Cell Tumor of the Pancreas”, or “Pancreatic Insulin-Producing Tumor”
Definition
- Insulin Secreting Neuroendocrine Tumor 1
- Due to an Abnormal Growth of the Beta Islet-Cells of the Pancreas 1
- There is a Single Report of an Insulin-Secreting Small Cell Carcinoma of the Cervix 2
- Is the Most Common Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor (PNET) 3
- *See Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor (PNET)
Distribution and Size
- Evenly Distributed Throughout Pancreas 4
- 7% are Multiple 5
- Most are Small (< 3 cm): 6
- < 1 cm: 24%
- 1-2 cm: 42%
- 2-3 cm: 30%
- > 3 cm: 4%
Malignancy
- Most are Benign (93%) 5
- 6% Have Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (MEN-1) 7
Epidemiology
- Median Age: 47-50 Years 6-8
- 57-60% are Female 6-8
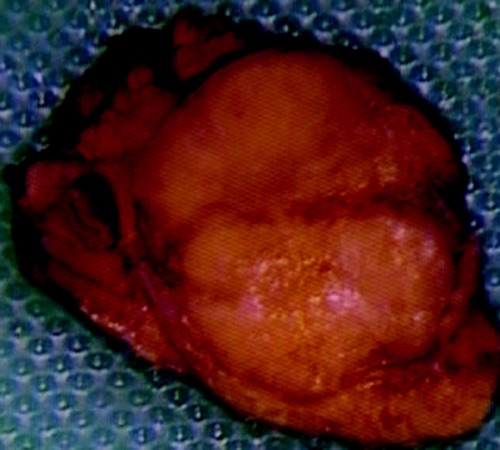
Insulinoma After Resection 9
Presentation
Symptoms 10-12
- Neuroglycopenic Symptoms:
- Confusion
- Visual Changes
- Unusual Behavior
- Sympathoadrenal Symptoms:
- Palpitations
- Diaphoresis
- Tremulousness
- Amnesia
- Weight Gain
Symptom Association with Diet 7
- Only Fasting Symptoms – 73%
- Often in the Morning Before Breakfast After Fasting Overnight
- Only Postprandial Symptoms – 6%
- Both Fasting and Postprandial Symptoms – 21%
Whipple’s Triad
- Used in the Diagnosis of Symptomatic Hypoglycemia (Not Exclusive to Insulinoma) 13,14
- Triad: 15
- Fasting Hypoglycemia (< 55 mg/dl)
- Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
- Symptomatic Relief with Glucose Correction
- Presence Suggests that Symptoms are Directly the Result of Hypoglycemia
Factitious Hypoglycemia
- Definition: Hypoglycemia Due to Exogenous Insulin Administration 16
- Often Due to Munchausen’s Syndrome 17
- Can Have a Similar Presentation and Should Be Excluded in the Workup of Insulinoma 18
Diagnosis
Diagnosis
- Primary Diagnosis Made by Demonstrating High Insulin Levels During a Spontaneous or Provoked Episode of Hypoglycemia 4
- Can Provoke by a 72-Hour Fast or Mixed-Meal Test
- Rule Out Factitious Hypoglycemia with a C-Peptide Level 19
- C-Peptide Levels Should be Elevated in the Setting of Insulinoma Commiserate with Insulin Secretion 19
- Low C-Peptide Levels Raises Concern for Exogenous Insulin Secretion
- Additionally Screen with Sulfonylurea and Meglitinide Levels
TNM Staging
- Same System Used for all Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors 20
- *See Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor (PNET)
Localization
- Initial Imaging: Noninvasive (CT or MRI) 21
- Somatostatin Receptor Imaging 22
- Consider if Initial Imaging Fails to Localize
- Insulinomas Demonstrate Relatively Low Somatostatin Receptor Expression (May Be More Difficult to Detect than Other PNETs) 23,24
- Options:
- Somatostatin (Octreotide) Receptor Scintigraphy (SRS) – Classic Test Used
- Functional PET Scan (Ga-68 DOTATATE) – Becoming More Prevalent with Higher Sensitivity
- If Noninvasive Imaging Fails: Invasive Imaging
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) – Generally Preferred Next Step 25
- Selective Arterial Calcium Stimulation Test (SACST) with Hepatic Venous Sampling 26
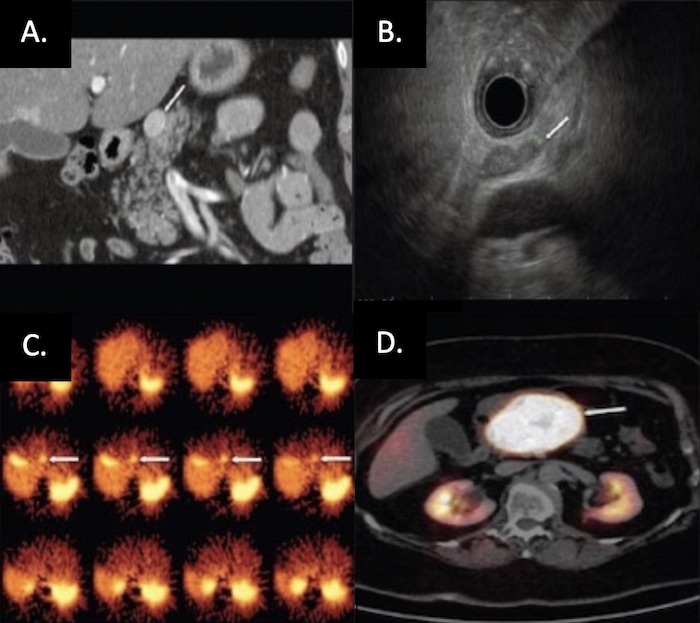
PNET on Imaging: (A) CT, (B) EUS, (C) SRS, (D) Functional PET 27
Treatment
Surgical Resection (Treatment of Choice) 4,28
- < 2-3 cm: Enucleation
- Additional Requirements:
- Single Lesion
- ≥ 2-3 mm From the Main Pancreatic Duct (Reduce Leak Risk)
- Well-Encapsulated
- No Local Invasion
- The Preferred Approach if Able
- Additional Requirements:
- > 2-3 cm: Surgical Resection
- Head/Neck: Pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Body/Tail: Distal Pancreatectomy (Concurrent Splenectomy if Malignancy is Suspected)
- Entire Pancreas: Total Pancreatectomy
Medical Management to Control Symptomatic Hypoglycemia
- Options:
- Diazoxide (Inhibits Insulin Release) – Preferred Agent 29-31
- Octreotide 31,32
- Everolimus 33
- Verapamil 31
- Phenytoin 34
- Used Preoperatively or for Patients that are Not Surgical Candidates or in Unresectable Metastatic Disease
Liver-Directed Therapy
- Resection of Metastases if Able
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) or Cryoablation 35
- Hepatic Artery Embolization 36
Additional Options in Surgically Unresectable Disease
- Tumor Embolization
- Chemotherapy 4
- Radiation Therapy 37,38
- Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Carcinomas Were Previously Considered to be Resistant to Radiation
References
- National Cancer Institute. NIH.
- Seckl MJ, Mulholland PJ, Bishop AE, Teale JD, Hales CN, Glaser M, Watkins S, Seckl JR. Hypoglycemia due to an insulin-secreting small-cell carcinoma of the cervix. N Engl J Med. 1999 Sep 2;341(10):733-6.
- Ro C, Chai W, Yu VE, Yu R. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: biology, diagnosis,and treatment. Chin J Cancer. 2013 Jun;32(6):312-24.
- Okabayashi T, Shima Y, Sumiyoshi T, Kozuki A, Ito S, Ogawa Y, Kobayashi M, Hanazaki K. Diagnosis and management of insulinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb 14;19(6):829-37.
- Service FJ, McMahon MM, O’Brien PC, Ballard DJ. Functioning insulinoma–incidence, recurrence, and long-term survival of patients: a 60-year study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1991 Jul;66(7):711-9.
- Pasieka JL, McLeod MK, Thompson NW, Burney RE. Surgical approach to insulinomas. Assessing the need for preoperative localization. Arch Surg. 1992 Apr;127(4):442-7.
- Placzkowski KA, Vella A, Thompson GB, Grant CS, Reading CC, Charboneau JW, Andrews JC, Lloyd RV, Service FJ. Secular trends in the presentation and management of functioning insulinoma at the Mayo Clinic, 1987-2007. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Apr;94(4):1069-73.
- Shao S, Zeng Z, Hu S. An observational analysis of insulinoma from a single institution. QJM. 2018 Apr 1;111(4):237-241.
- Alabraba E, Bramhall S, O’Sullivan B, Mahon B, Taniere P. Pancreatic insulinoma co-existing with gastric GIST in the absence of neurofibromatosis-1. World J Surg Oncol. 2009 Feb 13;7:18. (License: CC BY 2.0)
- Dizon AM, Kowalyk S, Hoogwerf BJ. Neuroglycopenic and other symptoms in patients with insulinomas. Am J Med. 1999 Mar;106(3):307-10.
- Service FJ, Dale AJ, Elveback LR, Jiang NS. Insulinoma: clinical and diagnostic features of 60 consecutive cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 1976 Jul;51(7):417-29.
- Harrington MG, McGeorge AP, Ballantyne JP, Beastall G. A prospective survey for insulinomas in a neurology department. Lancet. 1983 May 14;1(8333):1094-5.
- Martens P, Tits J. Approach to the patient with spontaneous hypoglycemia. Eur J Intern Med. 2014 Jun;25(5):415-21.
- Cazabat L, Chanson P. Hypoglycémie et insulinome [Hypoglycemia and insulinoma]. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2009 Sep;70 Suppl 1:S2-11.
- Desimone ME, Weinstock RS. Hypoglycemia. 2018 May 5. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, New M, Purnell J, Sahay R, Shah AS, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext.
- Bansal N, Weinstock RS. Non-Diabetic Hypoglycemia. 2020 May 20. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, New M, Purnell J, Sahay R, Shah AS, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext.
- Marks V, Teale JD. Hypoglycemia: factitious and felonious. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1999 Sep;28(3):579-601.
- Horwitz DL. Factitious and artifactual hypoglycemia. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1989 Mar;18(1):203-10.
- Pfützner A, Löbig M, Fortunato A, Forst T. Evaluation of a new fully automated one-step C-peptide chemiluminescence assay (LIAISON C-Peptid). Clin Lab. 2003;49(5-6):227-32.
- Bergsland EK, Woltering EA, Rindo G. Neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas. In: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed, Amin MB (Ed), AJCC, Chicago 2017. p.407. Corrected at 4th printing, 2018.
- Fedorak IJ, Ko TC, Gordon D, Flisak M, Prinz RA. Localization of islet cell tumors of the pancreas: a review of current techniques. Surgery. 1993 Mar;113(3):242-9.
- Nockel P, Babic B, Millo C, Herscovitch P, Patel D, Nilubol N, Sadowski SM, Cochran C, Gorden P, Kebebew E. Localization of Insulinoma Using 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT Scan. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Jan 1;102(1):195-199.
- Portela-Gomes GM, Stridsberg M, Grimelius L, Rorstad O, Janson ET. Differential expression of the five somatostatin receptor subtypes in human benign and malignant insulinomas – predominance of receptor subtype 4. Endocr Pathol. 2007 Summer;18(2):79-85.
- Peltola E, Vesterinen T, Leijon H, Hannula P, Huhtala H, Mäkinen M, Nieminen L, Pirinen E, Rönty M, Söderström M, Arola J, Jaatinen P. Immunohistochemical somatostatin receptor expression in insulinomas. APMIS. 2023 Apr;131(4):152-160.
- Rösch T, Lightdale CJ, Botet JF, Boyce GA, Sivak MV Jr, Yasuda K, Heyder N, Palazzo L, Dancygier H, Schusdziarra V, et al. Localization of pancreatic endocrine tumors by endoscopic ultrasonography. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jun 25;326(26):1721-6.
- Doppman JL, Miller DL, Chang R, Shawker TH, Gorden P, Norton JA. Insulinomas: localization with selective intraarterial injection of calcium. Radiology. 1991 Jan;178(1):237-41.
- Kartalis N, Mucelli RM, Sundin A. Recent developments in imaging of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Ann Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr-Jun;28(2):193-202. (License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0)
- de Carbonnières A, Challine A, Cottereau AS, Coriat R, Soyer P, Abou Ali E, Prat F, Terris B, Bertherat J, Dousset B, Gaujoux S. Surgical management of insulinoma over three decades. HPB (Oxford). 2021 Dec;23(12):1799-1806.
- Goode PN, Farndon JR, Anderson J, Johnston ID, Morte JA. Diazoxide in the management of patients with insulinoma. World J Surg. 1986 Aug;10(4):586-92.
- Gill GV, Rauf O, MacFarlane IA. Diazoxide treatment for insulinoma: a national UK survey. Postgrad Med J. 1997 Oct;73(864):640-1.
- Hirshberg B, Cochran C, Skarulis MC, Libutti SK, Alexander HR, Wood BJ, Chang R, Kleiner DE, Gorden P. Malignant insulinoma: spectrum of unusual clinical features. Cancer. 2005 Jul 15;104(2):264-72.
- Aparicio T, Ducreux M, Baudin E, Sabourin JC, De Baere T, Mitry E, Schlumberger M, Rougier P. Antitumour activity of somatostatin analogues in progressive metastatic neuroendocrine tumours. Eur J Cancer. 2001 May;37(8):1014-9.
- Ito T, Lee L, Jensen RT. Treatment of symptomatic neuroendocrine tumor syndromes: recent advances and controversies. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016 Nov;17(16):2191-2205.
- Hofeldt FD, Dippe SE, Levin SR, Karam JH, Blum MR, Forsham PH. Effects of diphenylhydantoin upon glucose-induced insulin secretion in three patients with insulinoma. Diabetes. 1974 Mar;23(3):192-8.
- Marx M, Trosic-Ivanisevic T, Caillol F, Demartines N, Schoepfer A, Pesenti C, Ratone JP, Robert M, Giovannini M, Godat S. EUS-guided radiofrequency ablation for pancreatic insulinoma: experience in 2 tertiary centers. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022 Jun;95(6):1256-1263.
- Linch F, Thompson S, Fleming C, Vella A, Andrews J. Hepatic Artery Embolization for Palliation of Symptomatic Hypoglycemia in Patients With Hepatic Insulinoma Metastases. J Endocr Soc. 2021 Oct 7;5(12):bvab149.
- Contessa JN, Griffith KA, Wolff E, Ensminger W, Zalupski M, Lawrence TS, Ben-Josef E. Radiotherapy for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009 Nov 15;75(4):1196-200.
- Strosberg J, Hoffe S, Gardner N, Choi J, Kvols L. Effective treatment of locally advanced endocrine tumors of the pancreas with chemoradiotherapy. Neuroendocrinology. 2007;85(4):216-20.

